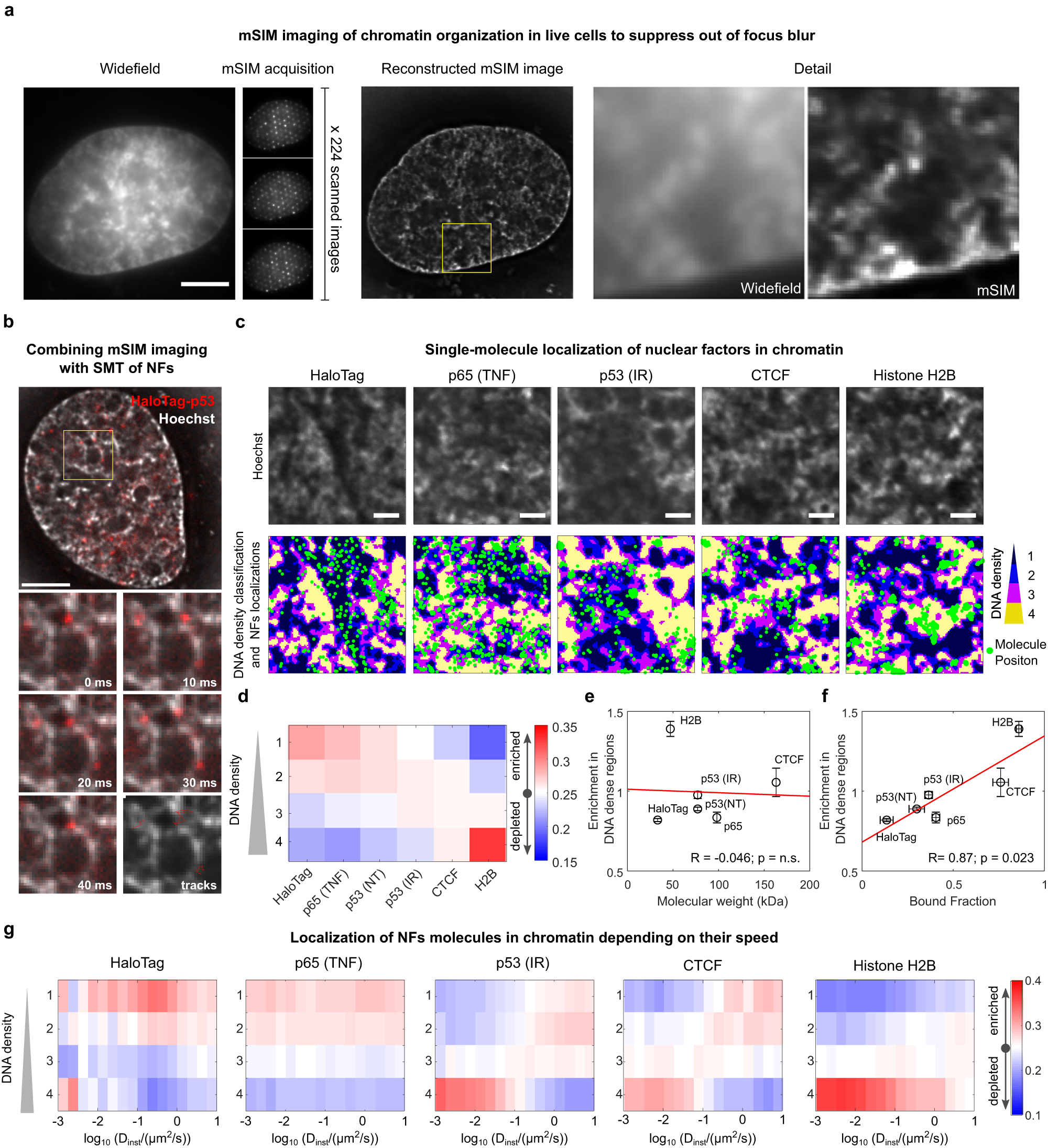
Chromatin organization drives the search mechanism of nuclear
4.8 (317) In stock

Asymmetric nuclear division in neural stem cells generates sibling nuclei that differ in size, envelope composition, and chromatin organization: Current Biology

Loss of lamin A function increases chromatin dynamics in the

Lamin A/C OE in the Drosophila larva muscle disrupts peripheral

Core Components of the Nuclear Pore Bind Distinct States of Chromatin and Contribute to Polycomb Repression: Molecular Cell

Dynamic 3D genome reorganization during senescence: defining cell states through chromatin

Dynamic microenvironments shape nuclear organization and gene
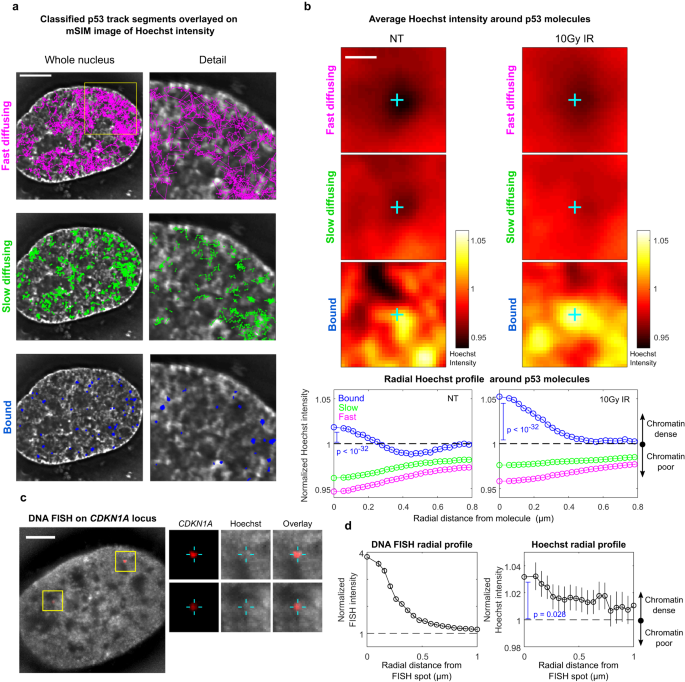
Chromatin organization drives the search mechanism of nuclear factors
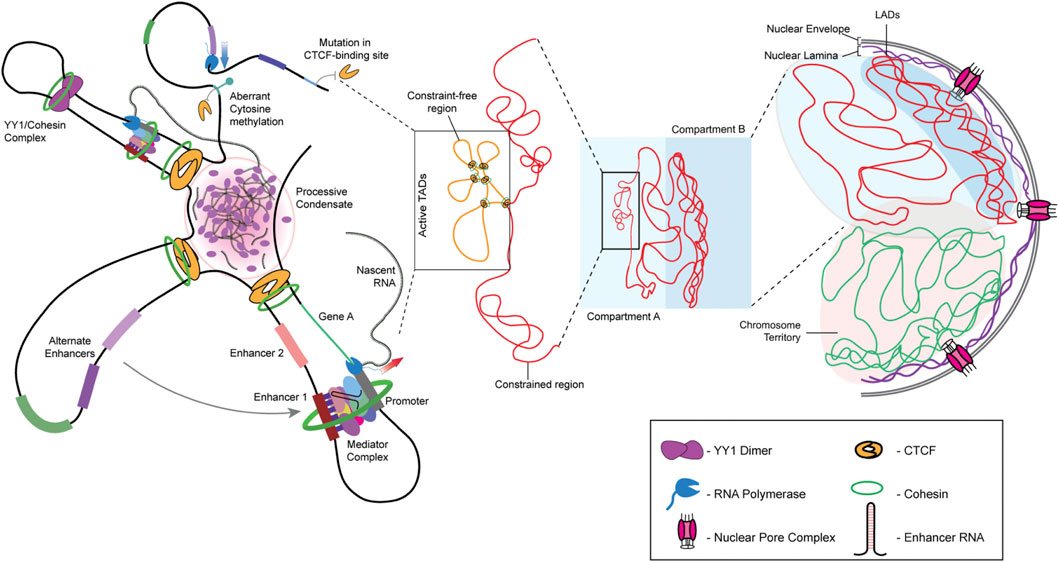
Frontiers Nuclear envelope, chromatin organizers, histones, and DNA: The many achilles heels exploited across cancers
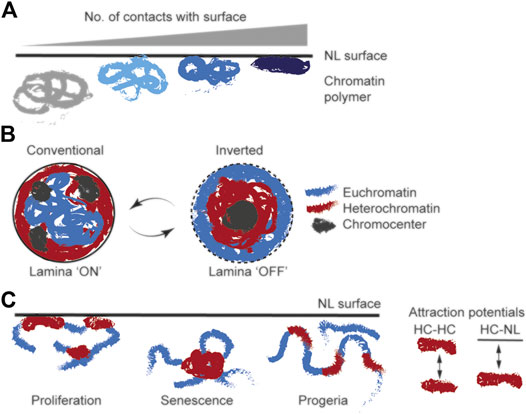
Frontiers Biology and Model Predictions of the Dynamics and Heterogeneity of Chromatin-Nuclear Lamina Interactions

Spatial relationship between CD chain and TADs. (A) RASER-FISH

Peripheral chromatin organization observed with His2Av and analysis of

The needle and the haystack: single molecule tracking to probe the








